Kerasで固有表現認識のf1スコアを計算する
一般に固有表現認識では、学習済みモデルの性能を評価するためにf1が使用されます。その際、評価はトークンごとではなくエンティティごとに行われるのが特徴となっています。
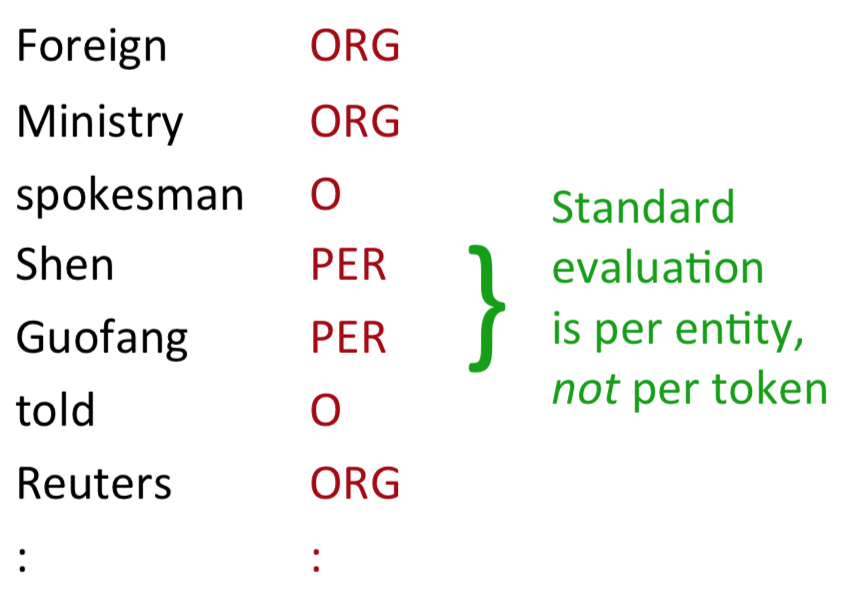
f1スコアを評価する関数は、多くの機械学習フレームワークに実装されています。しかし、そのターゲットは分類タスクであり、固有表現認識のような系列ラベリングタスクではありません。
幸いなことに、Kerasでは、コールバックを介して学習中に検証データにアクセスすることができます。したがって、コールバックを使うことで固有表現認識用にf1スコアを計算することができます。
以下は、各エポックの終わりにf1スコア、再現率、および精度を計算して出力するためのコードです。ここにはコードを載せましたが、実際には自分で実装する必要はありません。このコールバックはseqevalパッケージに含まれています。
import numpy as np from keras.callbacks import Callback from seqeval.metrics import f1_score, classification_report class F1Metrics(Callback): def __init__(self, id2label, pad_value=0, validation_data=None): """ Args: id2label (dict): id to label mapping. (e.g. {1: 'B-LOC', 2: 'I-LOC'}) pad_value (int): padding value. """ super(F1Metrics, self).__init__() self.id2label = id2label self.pad_value = pad_value self.validation_data = validation_data self.is_fit = validation_data is None def find_pad_index(self, array): """Find padding index. Args: array (list): integer list. Returns: idx: padding index. Examples: >>> array = [1, 2, 0] >>> self.find_pad_index(array) 2 """ try: return list(array).index(self.pad_value) except ValueError: return len(array) def get_length(self, y): """Get true length of y. Args: y (list): padded list. Returns: lens: true length of y. Examples: >>> y = [[1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]] >>> self.get_length(y) [1, 2, 3] """ lens = [self.find_pad_index(row) for row in y] return lens def convert_idx_to_name(self, y, lens): """Convert label index to name. Args: y (list): label index list. lens (list): true length of y. Returns: y: label name list. Examples: >>> # assumes that id2label = {1: 'B-LOC', 2: 'I-LOC'} >>> y = [[1, 0, 0], [1, 2, 0], [1, 1, 1]] >>> lens = [1, 2, 3] >>> self.convert_idx_to_name(y, lens) [['B-LOC'], ['B-LOC', 'I-LOC'], ['B-LOC', 'B-LOC', 'B-LOC']] """ y = [[self.id2label[idx] for idx in row[:l]] for row, l in zip(y, lens)] return y def predict(self, X, y): """Predict sequences. Args: X (list): input data. y (list): tags. Returns: y_true: true sequences. y_pred: predicted sequences. """ y_pred = self.model.predict_on_batch(X) # reduce dimension. y_true = np.argmax(y, -1) y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, -1) lens = self.get_length(y_true) y_true = self.convert_idx_to_name(y_true, lens) y_pred = self.convert_idx_to_name(y_pred, lens) return y_true, y_pred def score(self, y_true, y_pred): """Calculate f1 score. Args: y_true (list): true sequences. y_pred (list): predicted sequences. Returns: score: f1 score. """ score = f1_score(y_true, y_pred) print(' - f1: {:04.2f}'.format(score * 100)) print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred, digits=4)) return score def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs={}): if self.is_fit: self.on_epoch_end_fit(epoch, logs) else: self.on_epoch_end_fit_generator(epoch, logs) def on_epoch_end_fit(self, epoch, logs={}): X = self.validation_data[0] y = self.validation_data[1] y_true, y_pred = self.predict(X, y) score = self.score(y_true, y_pred) logs['f1'] = score def on_epoch_end_fit_generator(self, epoch, logs={}): y_true = [] y_pred = [] for X, y in self.validation_data: y_true_batch, y_pred_batch = self.predict(X, y) y_true.extend(y_true_batch) y_pred.extend(y_pred_batch) score = self.score(y_true, y_pred) logs['f1'] = score id2label = {1: 'B-LOC', 2: 'I-LOC'} f1score = F1Metrics(id2label)
使い方は簡単です。モデルを定義し、fitメソッドにコールバックを追加するだけです。
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
validation_data=(x_valid, y_valid),
epochs=1,
batch_size=32,
callbacks=[f1score])
学習中の出力は以下のようになります。
Epoch 1/1
541/541 [==============================] - 46s 85ms/step - loss: 9.5729
- f1: 53.24
precision recall f1-score support
PER 0.5754 0.4484 0.5040 1617
ORG 0.3798 0.4395 0.4075 1661
MISC 0.4202 0.4387 0.4293 702
LOC 0.6886 0.7650 0.7248 1668
avg / total 0.5320 0.5381 0.5315 5648
フォーマットはscikit-learnのclassification_report関数に似せているので使いやすいのではないかと思います。
fit_generatorで使う場合はF1Metricsの初期化メソッドに検証用データを渡してください。これは、fit_generatorを使った場合にコールバック内部から検証用データにアクセスできない仕様によるものです。